AMAZON multi-meters discounts AMAZON oscilloscope discounts
[Note: various equations denoted by "e." are not yet avail., but coming soon.]
1. Introduction to Ground Grid Design
The grounding or earthing system is a total set of measures used to connect the electrically conductive components of a power system to earth. The design of electrically safe workplaces has been developed at considerable depth in the field of grounding system design for electrical substations. The effects of potentials and currents on workers in substations has been carefully evaluated with regard to the electrical properties of the human body and the magnitudes of electrical current and voltage which are harmful, resulting in designs which are much safer than they otherwise would have been. This process has been greatly helped by industry standards which set forth design procedures and calculation techniques which will result in a safe design within the selected parameters.
The grounding system is an essential part of both high- and low-voltage electrical power networks, and has at least four important roles:
1. To protect against lightning by:
• providing an electrically and mechanically robust path for current to flow to ground;
• limiting potential differences across electrical insulation on stricken towers;
• reducing the number of flashovers that occur.
2. To minimize energy for correct operation of the power system by
• providing unambiguous identification of faults, so that the correct protection systems operate;
• providing low zero-sequence impedance for return of the unbalanced fraction of AC system currents.
3. To minimize energy to ensure electrical safety by:
• rapidly identifying system faults, leading to reduce fault duration;
• limiting touch or step voltages to levels that restrict body currents to safe values.
4. To eliminate some hazards and reducing the energy of others to contribute to electromagnetic compatibility.
All of these functions are provided by a single grounding system. Some elements of this system may have specific electrical purposes, but all elements are normally bonded or coupled together, forming one system to be designed or analyzed.
2. Summary of Ground Grid Design Procedures
Design of a ground grid is part of the overall design of a substation. The ground rods are driven in and the ground grid constructed before the surface layer of gravel is poured and the above-ground portions of the substation constructed. The design goals, as listed in IEEE Standard 80-2000 are:
"To provide means to dissipate electric currents into the earth without exceeding any operating and equipment limits." "To assure that a person in the vicinity of grounded facilities is not exposed to the danger of critical electrical shock." The critical parameters in the design of the ground grid are listed in Table 1. The ground grid procedure is listed in Table 2.
Table 1 Critical Parameters in Ground Grid Design Symbol Name Equation Typical values Units
===========
Table 2 Sample Procedure for Ground Grid Design
Step Description Results 1 Site survey, soil resistivity test A, ? 2 Conductor size, zero sequence current, fault-clearing time Amm2, 3I0, tc 3 Step and touch potentials Estep, Etouch 4 Conductor loop design, conductor spacing, ground rod locations Various dimensions; 5. Estimated resistance of grounding system in uniform soil RG 6 Recalculate ground current and fault duration a IG, tf 7 If GPR < tolerable touch voltage, go to step 12 IGRG < Etouch 8 If GPR > tolerable touch voltage, calculate mesh and step voltages Em, Es, various K 9 If mesh voltage < tolerable touch voltage, go to step 10, otherwise go to step 11 Em < Etouch 10
If step voltage < tolerable touch voltage, go to step 12, otherwise go to step 11 Es < Etouch 11
If mesh or step voltage > tolerable touch voltage, revision of design is required
Decision 12 Add equipment ground conductors, additional grid conductors, ground rods as needed Final design a Based on current splits, worst-case fault and future expansion.
===========
2.1 Site Survey
The shape and area of the substation are determined and ground resistivity measurements are taken to determine.
2.2 Conductor Sizing
The most important factor in terms of overcurrent phenomena is the sizing of the ground grid conductors.
The design procedure makes two assumptions:
1. Adiabatic heating of the conductor. The instantaneous power per unit length is
eq.1
The joule heating is…
eq.2
2. The thermal capacity per unit volume remains constant (this is usually true for short fault durations). The temperature rise from ambient to the maximum conductor temperature occurs in the fault clearing time (Sverak, 1981).
eq.3
eq.4
[...]
This is illustrated in FIG. 1 for several ratios.
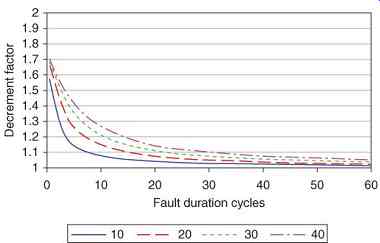
FIG. 1 Decrement factor versus fault duration for four different X/R ratios.
The conductors of a ground grid should be designed for a particular maximum fault current, ratio, and clearing time. Examples are shown in Table 3. A safety factor is usually applied in the design to allow for future growth in fault current magnitudes.
=======
Table 3 Fusing Currents in Symmetrical kA for Annealed Soft-Drawn 100% Conductivity Copper Conductors Versus X/R Ratio. All Clearing; Times 0.5 s.
========
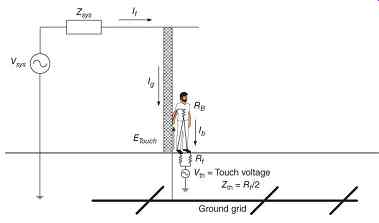
If a person standing on a surface whose potential has risen owing to the flow of ground current touches a grounded object, they experience a touch voltage ( FIG. 2). A Thévenin equivalent circuit of the person exposed to the touch voltage is also shown.
Whether the touch voltage is hazardous can be determined by comparison with the calculated safe level of touch voltage for that substation.
Similarly, if a person is standing on the surface, and the flow of ground current causes a dangerous voltage drop to occur between their feet, they are exposed to a step voltage ( FIG. 3). A Thévenin equivalent circuit of the person exposed to the step voltage is also shown. The safe levels of step and touch potentials are defined on the basis of a person's body weight and the length of exposure. The usual standards used are for 50 and 70 kg (110 and 154 lb) body weights. The step and touch potentials are calculated using eq.11.
where...
X = either "step" or "touch" W = either "50" or "70"
= the typical resistance of the human body
m = 0 for metal-to-metal touch voltage, 1 otherwise A = 6 for "step" or 1.5 for "touch"
= the resistivity of the surface material in
= if there is no surface layer.
Normally
= 0.116 for "50" or 0.157 for "70"
= the duration of the shock current, s
= the surface layer-derating factor
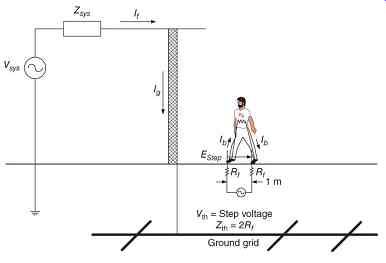
FIG. 3 Step voltage will approach 1.0 as hs ? increases and as s ? . It will
approach 0 as s? 0.
…if there is no surface layer, otherwise an approximate formula (within 5% of computer models) may be used:
...eq.12 ... where
= depth of the surface material in m will approach 1.0 as increases and as .
It will approach 0 as ....
2.4 Ground Grid Layout
Using the shape and area previously determined, a grid is laid out at a depth, , with spacing , and total length of buried conductor. If ground rods, unequal spacing, or a shape other than square are used, other parameters will apply as well.
2.5 Ground Resistance Calculation
The resistance of the grounding grid, , can be estimated using Sverak's equation:
eq.13
... where…
= resistance in Z = earth resistivity in
= total length of buried conductors in m A = total area of the grid in .
2.6 Calculation of Maximum Grid Current
The maximum current that is used in ground potential rise calculations is not always the same as the maximum current used for conductor sizing. The maximum grid current is [...]
...is the station ground impedance in is the impedance of the overhead static wire for the transmission line in is the impedance of the overhead static wire for the distribution line in…
2.7 Calculation of Ground Potential Rise (GPR)
The ground potential rise is eq.19.
This is compared with the touch potentials and…. If it is larger, the mesh voltage is calculated.
2.8 Calculation of Mesh Voltage
The basis of the design procedure is to minimize the "mesh voltage," which is the maximum touch voltage within the area of the ground grid, which is taken to mean at the center of the corner mesh, the usual point of maximum.
eq.20
...where is the earth resistivity in is the geometrical factor, defined as:[...]
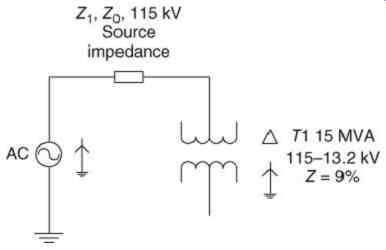
FIG. 4 Single-line diagram for example.
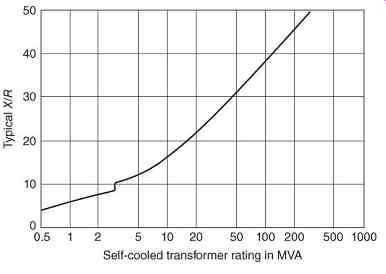
FIG. 5 X/R ratio of transformers.
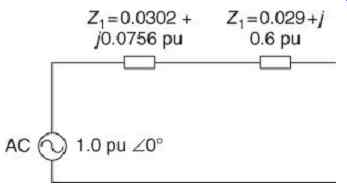
FIG. 6 Positive sequence equivalent circuit.
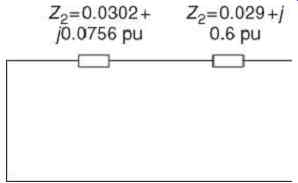
FIG. 7 Negative sequence equivalent circuit.
The zero sequence equivalent circuit is shown in FIG. 8.
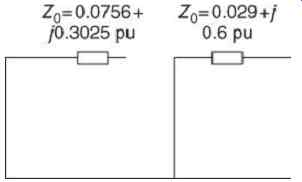
FIG. 8 Zero sequence equivalent circuit.
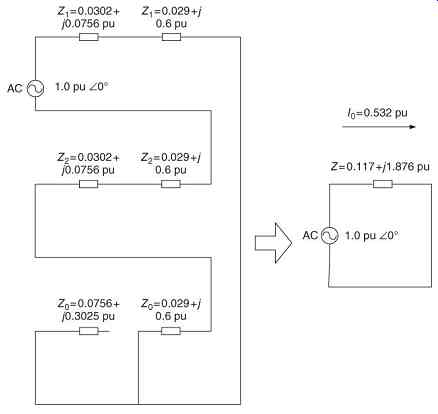
FIG. 9 Symmetrical components solution of 115 kV single-line-to-ground ground
fault.
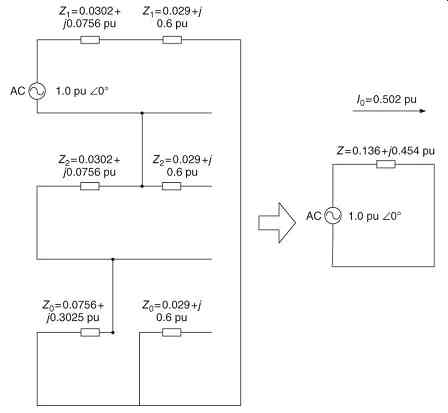
FIG. 10 Symmetrical components solution of 13.2 kV single-line-to-ground
ground fault.