AMAZON multi-meters discounts AMAZON oscilloscope discounts
The simplest inverter to understand is the single-phase inverter, which takes a dc input voltage and converts it to single-phase ac voltage. The main components of the inverter can be either four silicon controlled rectifiers (SCRs) or four transistors. Fig. 1 shows a typical inverter circuit that uses four SCRs, and Fig. 2 shows a typical inverter circuit that uses four transistors. Originally called a dc-link converter, now it's simply called an inverter.
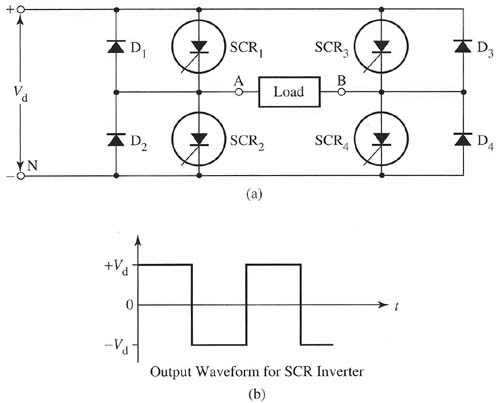
Above: Fig. 1 (a) Electrical schematic of a typical inverter circuit that
uses four silicon controlled rectifiers (SCRs). (b) Output waveform for
SCR inverter.
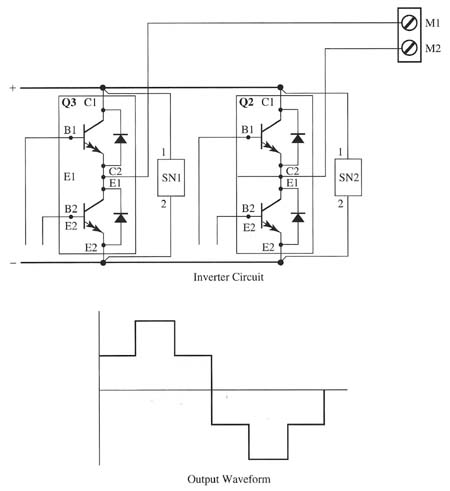
Above: Fig. 2 Electrical schematic of a transistor inverter with the output
waveforms for the ac voltage.
The diagram in Fig. 1 shows four SCRs used in the inverter circuit. In this circuit SCR1, and SCR4 are fired into conduction at the same time to provide the positive part of the ac waveform and SCR2 and SCR3 are fired into conduction at the same time to provide the negative part of the ac waveform. The waveform for the ac output voltage is shown in this figure -- notice that it's an ac square wave. A phase-angle control circuit is used to determine the firing angle, which provides the timing for turning each SCR on so that they provide the ac square wave. The load is attached to the two terminals where the ac square wave voltage is supplied.

