Shelving shouldn’t sag or bend under the weight of a load. The guidelines and chart below will help you select the appropriate materials for your project. Note that there are a number of ways to deal with a too-heavy load: you can reinforce the shelf, change the material you construct it of, choose a thicker or wider piece of stock, or shorten the span. The general guideline is: the thinner, the narrower in width, and the longer the piece of stock, the more apt it is to bend.
Materials Lumber: is the most rigid material and therefore least apt to bend under loads. Plywood: is less rigid than lumber and thus more apt to bend. Particle board and hardboard: are least rigid and are thus apt to bend or even break under loads. |
 |
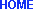
Load Types In designing a shelf, consider not only the weight (load) but also how it will be distributed, and select a shelf design, a construction method, and materials that have sufficient rigidity to avoid sagging. The potential for sagging will vary with the way the load is placed on the shelf. |
 |
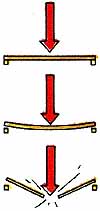
Ways to Reinforce a Sagging Shelf Be conservative in deciding the length of shelf spans; if there is a possibility of sagging, use one of the reinforcing methods shown here. Apply lumber to one or both long edges. Add mid-span supports as needed. Add support around shelf edges. |
 |
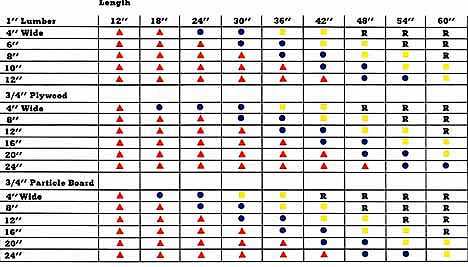
Table below shows: Load Capacities
Light Load -- yellow dot -- (10 - 15 pounds. Example: towels.)
Average load -- black dot -- (15 to 25 pounds. Example: mix of canned and boxed food staples.)
Heavy load -- red triangle -- (25 to 50 pounds. Example: LPs, LaserDiscs, Books).)
Reinforce -- R -- (You’ll need to reinforce a shelf of these dimensions.)
Previous: Materials
Next: Sizing Up Your
Space
ALL ARTICLES in this Guide:
DIY and Custom-Made Storage Solutions: Components You Can Build for Home, Office ... as a Hobby or for Sale (Profit, earn Income)